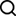Your database isn’t just a storage solution—it’s the backbone that powers your entire ecosystem. Whether you’re running a small e-commerce site or managing enterprise-level operations, the way you design and structure your database directly impacts everything from user experience to your bottom line.
Design flaws can lead to reduced performance, data inconsistencies, security breaches, or increased maintenance efforts. The goal of sound database design is to strike a balance between usability, data security, and performance across stakeholders.
Essentials of Database Design
Database design refers to the structured process of creating a database to efficiently store, manage, secure, and process data. A well-architected database serves as a centralized hub that eliminates data silos across departments. Instead of marketing, sales, and customer service maintaining separate spreadsheets with conflicting information, everyone works from the same accurate source.
This unified approach doesn’t just improve efficiency—it enables the kind of comprehensive modeling and analytics that drive strategic decisions.
The Five Pillars of Effective Database Design
1. Clarity Through Simplicity
The best database designs are intuitive. When your development team can understand the structure at a glance, they spend less time deciphering relationships and more time building features that matter to your users.
In practice: Rather than cramming customer information, order details, and product data into one massive table, create separate, focused tables:
- Customer table – manages personal information
- Orders table tracks purchases
- Products table manages inventory
Clean, logical separation in database design makes everything easier to work with.
2. Bulletproof Data Integrity
Data integrity ensures your information remains accurate and consistent across all operations. It’s about building trust in your data that enables confident decision-making.
Integrity rules:
- Entity integrity ensures every record has a unique identifier
- Referential integrity maintains valid relationships between tables
- Domain integrity enforces appropriate data types and constraints
- Access controls protect sensitive information from unauthorized changes
In practice: An e-commerce system should not allow an order to exist without a valid customer account, and product inventory should not show negative quantities.

3. Strategic Redundancy Elimination
Data redundancy creates a maintenance nightmare. When the same information exists in multiple places, updates become error-prone, costs increase for storage and marketing, and inconsistencies inevitably creep in.
Normalization solves this by storing each piece of information exactly once and using relationships to connect related data. Instead of repeating a customer’s address in every order record, you store it once in the customer table and reference it through relationships.
4. Flexibility and Scalability
Business requirements evolve, and your database needs to evolve with them. Smart database design strategies anticipate growth and change without requiring complete rebuilds.
Scalability considerations:
- New features should be integrated smoothly without disrupting existing functionality
- The system should maintain performance as data volumes grow
- Schema modifications should be straightforward and low risk
In practice: When an online retailer wants to add subscription services to their existing one-time purchase model, a flexible database design accommodates this expansion without restructuring the entire system.
5. Performance
Performance optimization involves strategic indexing, efficient query patterns, and smart data organization.
Key performance strategies:
- Strategic indexing on frequently queried columns
- Table partitioning for large datasets
- Query optimization through clean table relationships
- Caching strategies for frequently accessed databe
Normalization
Normalization is a critical step in database design aimed at minimizing redundancy and ensuring data consistency. It involves splitting the database into smaller, logically connected tables, where each table focuses on a specific subject or entity.
This approach improves data integrity and simplifies maintenance. However, it can also impact query performance, which is why a balance between normalization and performance should be considered.
Data Enrichment – More Personal and Effective
Good database design services go beyond storing transactional data. By enriching customer records with demographic, geographic, and behavioral data, a simple contact list turns into a powerful marketing and analytics platform. This enhanced dataset enables personalized experiences, targeted campaigns, and predictive analytics that drive revenue growth.
Analytics and Modeling Integration
Your database design should support not just day-to-day operations but also advanced analytics. This means structuring data in ways that facilitate customer segmentation, predictive modeling, and trend analysis. The goal is to create a complete view of your customers that reveals opportunities for omnichannel marketing, cross-selling, up-selling, and retention strategies.
Getting Database Design Right
Database design is a strategic business decision that impacts every aspect of your operations. The right approach balances immediate needs with long-term growth.
Whether you’re building from scratch or optimizing existing systems, database consultants can help you avoid costly mistakes and build a foundation that supports your business goals. Anchor’s design database consultants bring experience from diverse industries and can identify optimization opportunities that might not be obvious to internal teams.
The investment in proper database design consultants pays dividends through improved performance, reduced maintenance costs, enhanced security, and the ability to respond quickly to market opportunities.
Contact our database design consultants for a free assessment or call (800) 452-2357.